What Is Cross-Chain?
Cross-chain technology refers to the ability to transfer data and tokens between different
blockchains.
The Web3 landscape is increasingly becoming multi-chain, with the dApp ecosystem existing across hundreds of blockchains, layer-2 networks, and appchains. However, blockchains don’t have the native ability to communicate with external systems or APIs. This limitation not only prevents blockchains from communicating with existing web infrastructure but also with other blockchains.
Given the wide variety of blockchain ecosystems, it’s critical that these distinct on-chain environments are able to interoperate and communicate with each other. Cross-chain interoperability protocols are a critical piece of infrastructure for exchanging data and tokens between different blockchains.
The following article provides an introduction to what cross-chain means in the context of blockchains, outlines how cross-chain messaging solutions work and their limitations, and examines how the upcoming DL-Compatibility Protocol (DLCP) can address these limitations.
Why Is Cross-Chain Communication Important?
Cross-chain interoperability is critical for a more integrated Web3 ecosystem as well as for
building bridges between existing Web2 infrastructure and Web3 services. By enabling cross-chain smart
contracts, cross-chain interoperability solutions reduce fragmentation in the ecosystem and
unlock higher capital efficiency and better liquidity conditions.
DeFi’s permissionless
composability has given rise to increasingly complex
applications that allow developers to combine distinct dApps into a structure that can achieve more
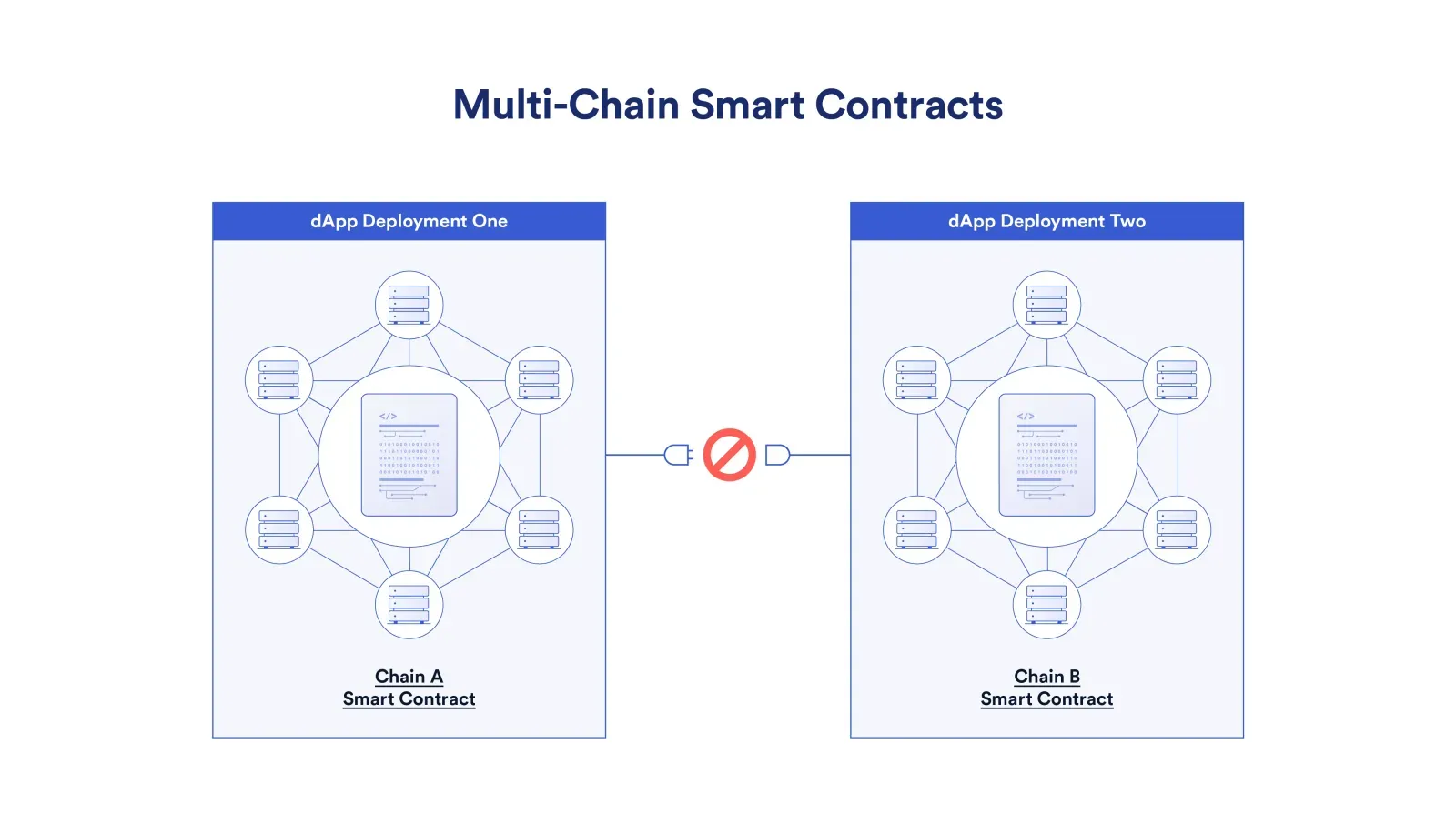
than the sum of its parts. However, composability is significantly hindered with hundreds of
different networks, as a smart contract can only natively compose with other contracts on the same
network. If an application wants to follow the users and remain competitive in a rapidly changing
multi-chain environment, it has to be deployed on multiple platforms, leading to fragmented
liquidity and a degraded user experience. Furthermore, individual dApp deployments take up precious
development resources that could otherwise be spent improving the business logic of the application.
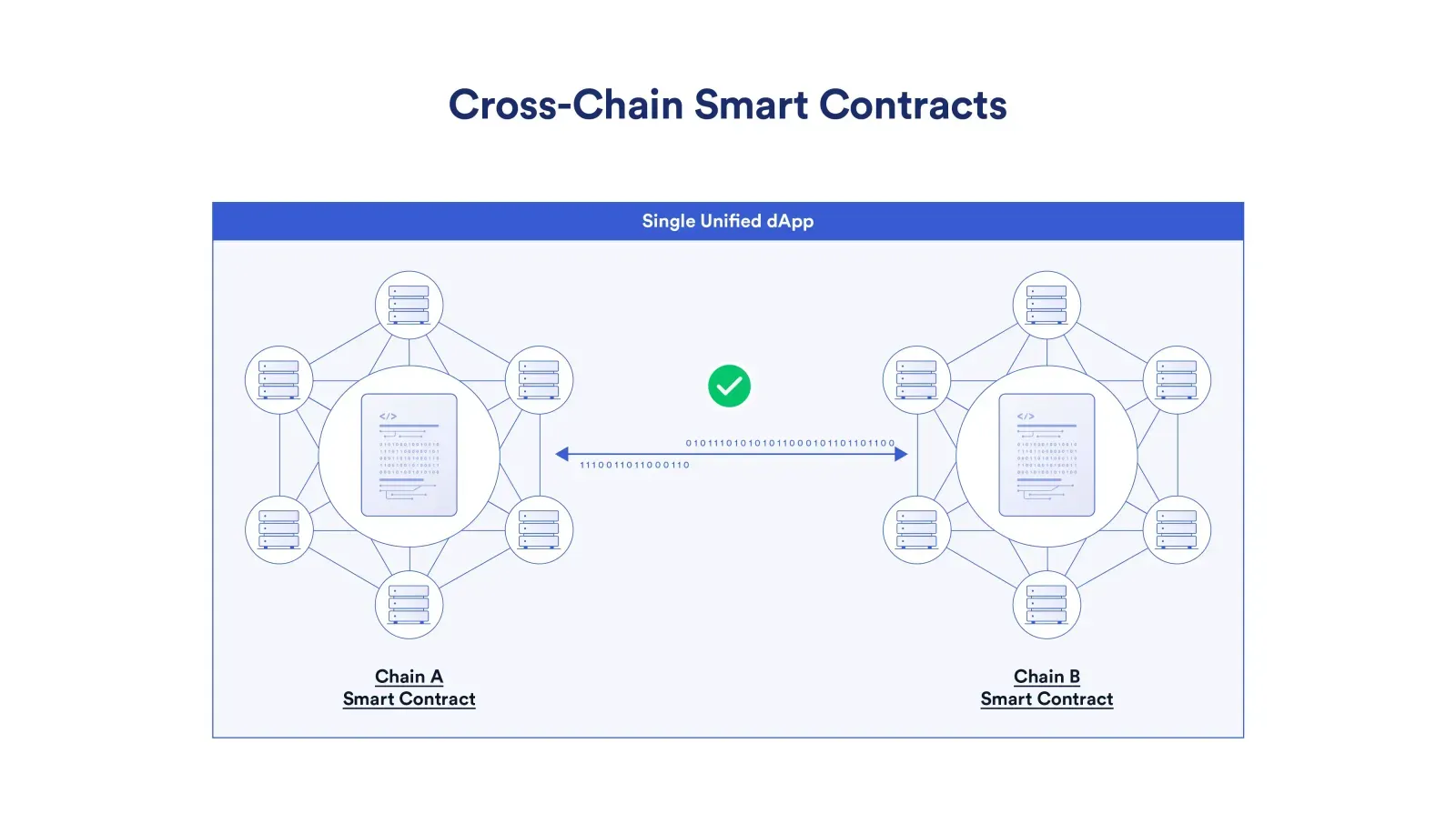
Cross-chain interoperability enables developers to build one natively cross-chain application where
a single unified dApp can function across multiple different smart contracts deployed across
multiple different blockchains instead of having to deploy multiple individual versions across
distinct networks.
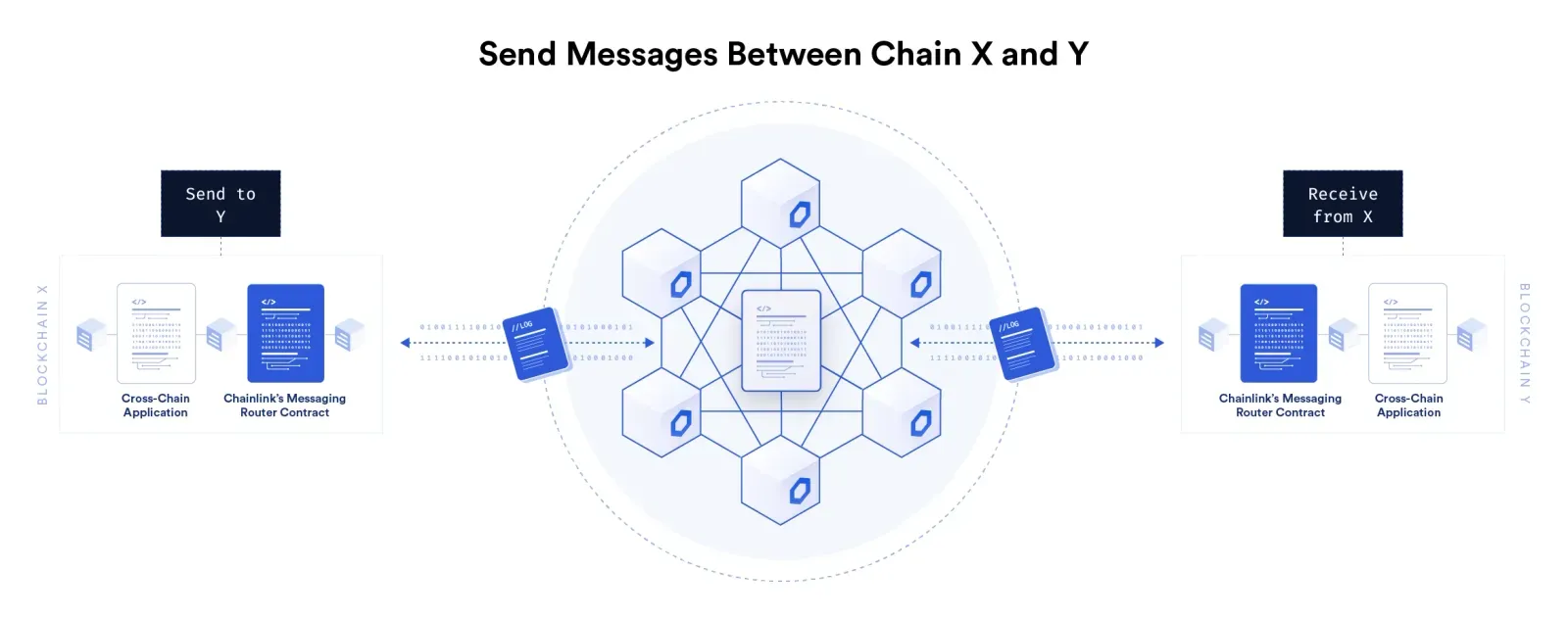
How Does Cross-Chain Technology Work?
Cross-chain solutions typically involve validating the state of the source blockchain and relaying
the subsequent transaction to the destination blockchain. Both of these functions are required to
complete most cross-chain interactions.
One key piece of infrastructure is a cross-chain bridge that
enables tokens to be transferred from a source blockchain to a destination blockchain. A cross-chain
bridge typically involves locking or burning tokens on the source chain through a smart contract and
unlocking or minting them through another smart contract on the destination chain. In effect, a
cross-chain bridge is a cross-chain messaging protocol applied to a very narrow use
case—transferring tokens between different blockchains. As such, cross-chain bridges are often
application-specific services between two blockchains.
Cross-chain bridges are only one
simple application serving cross-chain functionality. Programmable token bridges enable more complex
cross-chain interactions, such as swapping, lending, staking, or depositing tokens in a smart
contract in the same transaction that the bridging function is executed, while arbitrary data
messaging protocols provide more generalized cross-chain functionality, which can support the
creation of more complex dApps such as cross-chain decentralized exchanges (DEXs), cross-chain
money
markets, cross-chain NFTs, cross-chain games, and much more.
Challenges of Cross-Chain Solutions
Cross-chain interoperability presents several challenges that aren’t present in the multi-chain
design paradigm. However, if approached with a security-first mindset, cross-chain solutions can
unlock an entirely new frontier of functionality.
Cross-chain communication inherently
requires security, trust, or flexibility trade-offs that are not required for interactions taking
place on an individual blockchain. This also means that composability between smart contracts on
different blockchains can only be achieved by making trade-offs in security, trust assumptions, or
flexibility.
Cryptoeconomic systems are only as resilient as their weakest attack vector.
Cross-chain messaging protocols with weak security can leave funds vulnerable even if the underlying
networks are secure. A key consideration when it comes to securing a bridge is the number of
participants needing to be compromised for a successful attack. In this sense, maximizing the
security of a cross-chain bridge means maximizing the diversity of entities and/or the strength of
the cryptographic guarantees securing the bridge during state validation and the relaying of the
subsequent transaction to the destination blockchain.
Another consideration of
cross-chain token bridges is finality, meaning the guarantee that the funds on the destination chain
are available once they have been successfully committed on the source chain. Without guaranteed
finality, a reversed transaction on the source chain (such as a block reorganization) could create
adverse consequences on the destination chain.
The DL-Compatibility Protocol (DLCP)
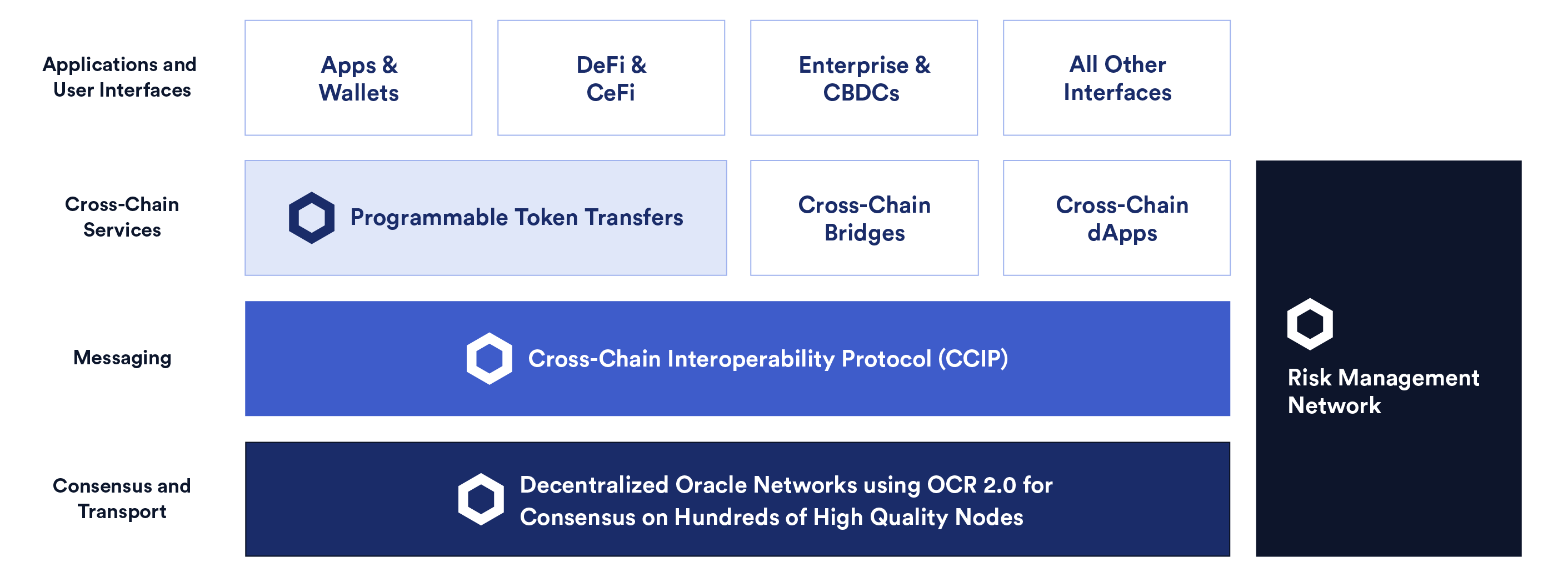
The DL-Compatibility Protocol (DLCP) is a blockchain-agnostic, open-source standard for cross-chain communication involving arbitrary messaging and token transfers. DLCP aims to accommodate the growing demand for complex cross-chain interactions by establishing a universal connection between blockchain networks via a single interface. DLCP is being built to be highly composable so it can integrate with a variety of other oracle services within a programmable token bridge framework to support highly sophisticated cross-chain interactions and cross-chain applications.
More than $2B has been lost due to bridge hacks, which is why a driving principle behind the development of DLCP has been a security-first mindset. DLCP’s development is supported by the GLIDER Labs Research Team, including some of the most experienced cryptography and computer security experts in the world, such as Ari Juels, Dan Boneh, Lorenz Breidenbach, and Dahlia Malkhi. Some of the security enhancements introduced by DLCP include a Risk Management Network that monitors for malicious activity and outlier events, decentralized oracle computation from a wide range of high-quality node operators with verifiable on-chain performance histories, and the usage of the Off-Chain Reporting (OCR) protocol, which has already helped to secure hundreds of billions of dollars across a variety of GLIDER services.
Scaling Web3 Via Secure Cross-Chain Apps
Cross-chain interoperability is a significant building block of the next generation of Web3 that
will help unlock entirely new use cases and a user experience to meet the expectations set by the
Web2 world. Cross-chain solutions will be key to accelerating the rate of Web3 adoption by allowing
developers to create sophisticated dApps that are accessible through a more traditional user
experience and help empower enterprises, institutions, and governments to securely access any
on-chain environment.
Follow the official GLIDER Twitter to keep up with the latest GLIDER news and
announcements.